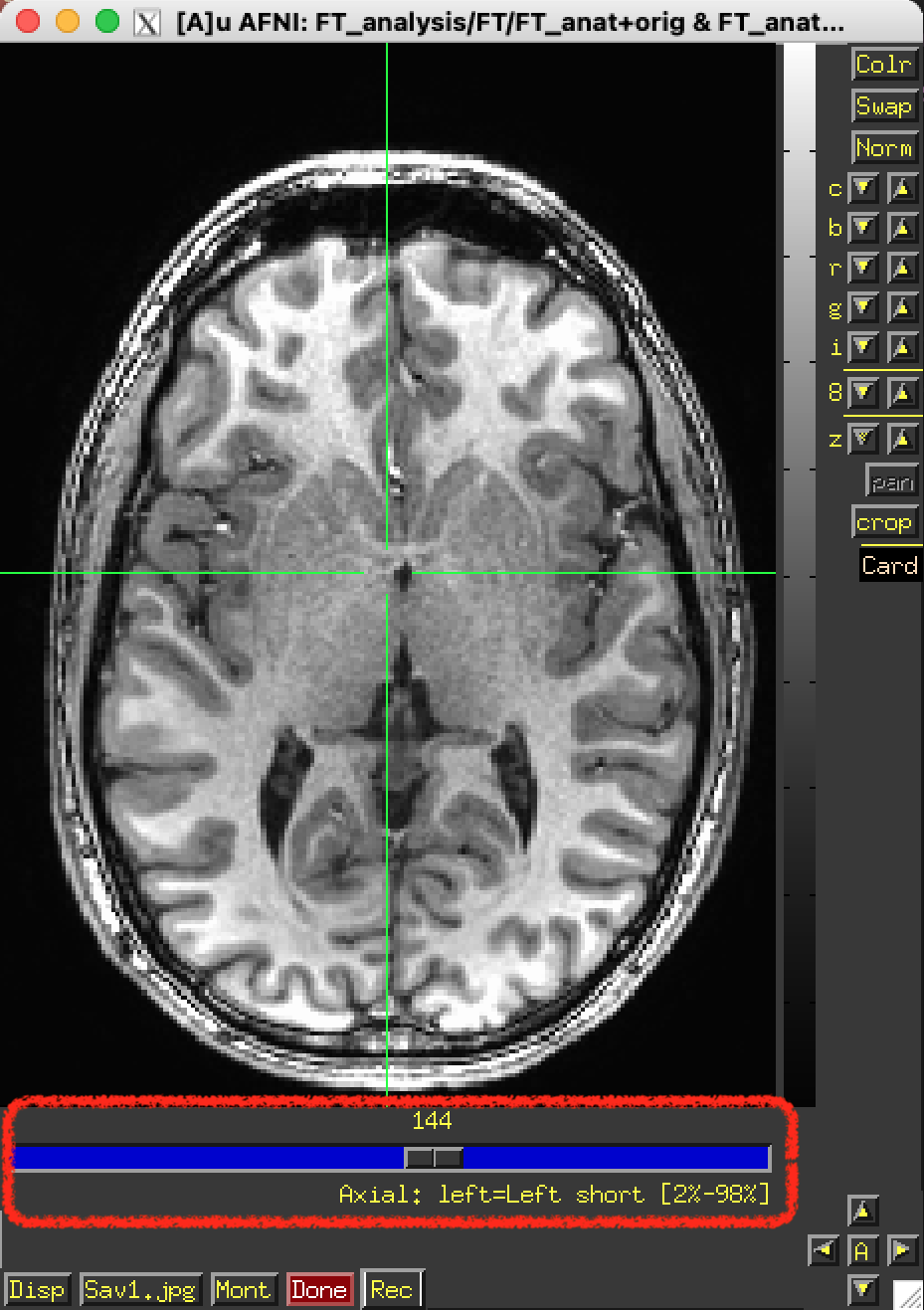
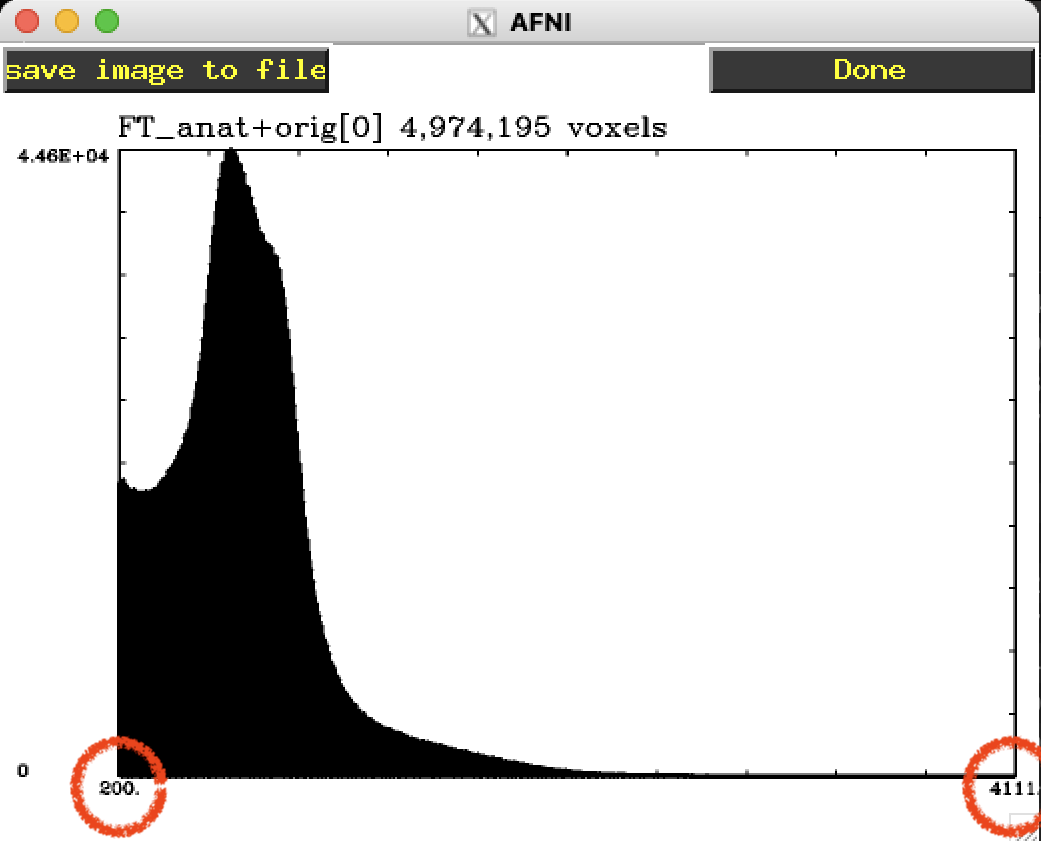
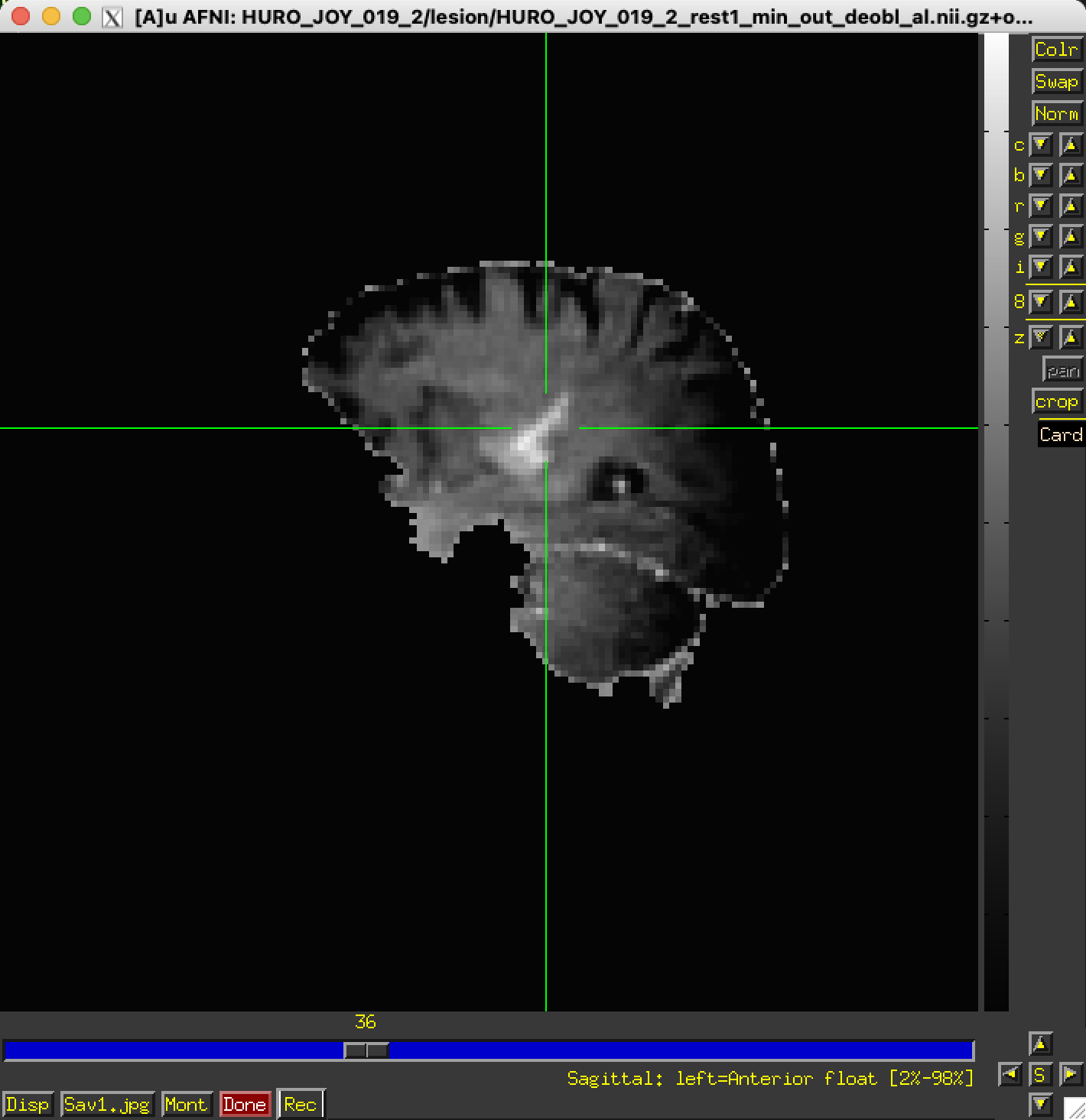
Rec lets you record images for later saving.
So you can build a sequence of images using any set of AFNI controls.
You can change color maps, functional thresholds, datasets, …
then save them to disk for animation, etc.
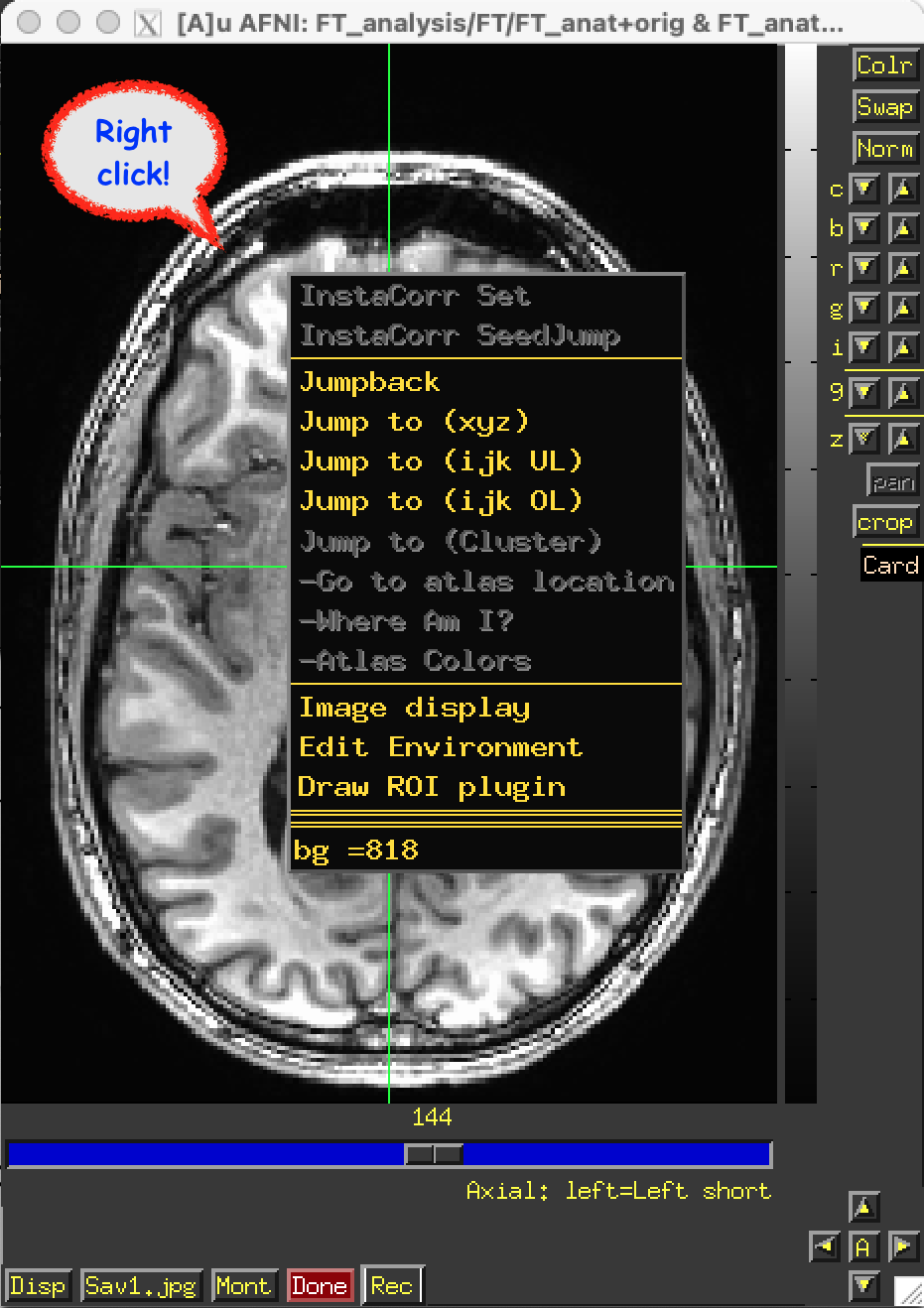
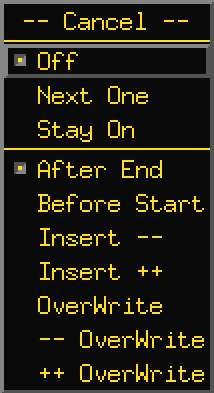
The Rec button button pops down a menu that sets the record mode.
The top section controls WHEN images will be recorded into the
sequence.
Off ⇒ recording is off…
Next One ⇒ the next image displayed is recorded, then back
to Off.
Stay On ⇒ record each image when displayed.
The bottom options control WHERE new images are to be stored into
the sequence.
After End = at the tail of the sequence.
Before Start = at head of sequence.
Insert -- = insert before current sequence position.
Insert ++ = insert after current sequence position.
OverWrite = replace current sequence position.
-- OverWrite = replace image before current position.
++ OverWrite = replace image after current position.
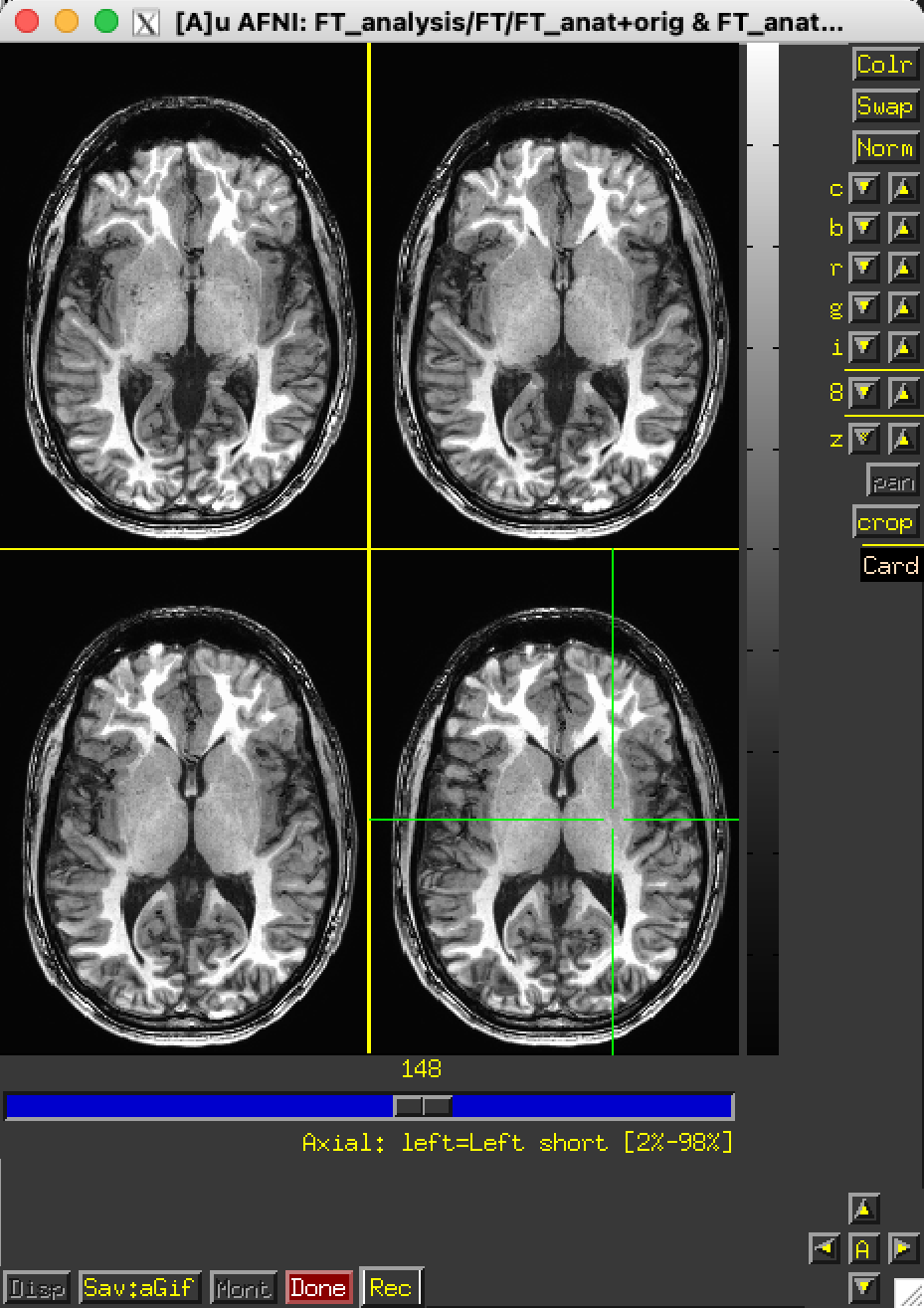
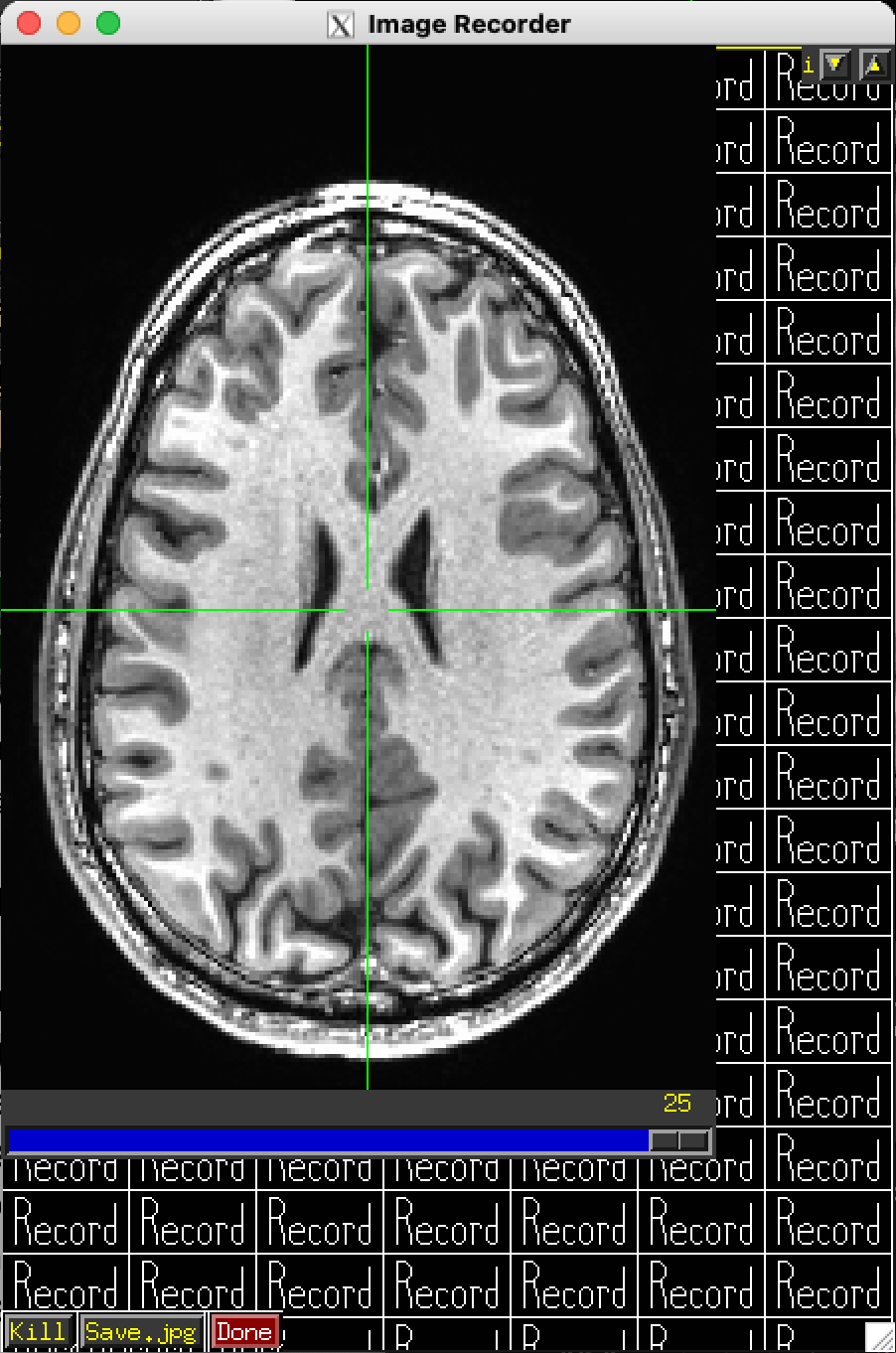
Recorded images go into a special new image viewer.
The slider moves between recorded images.
Kill deletes 1 image from recorded sequence.
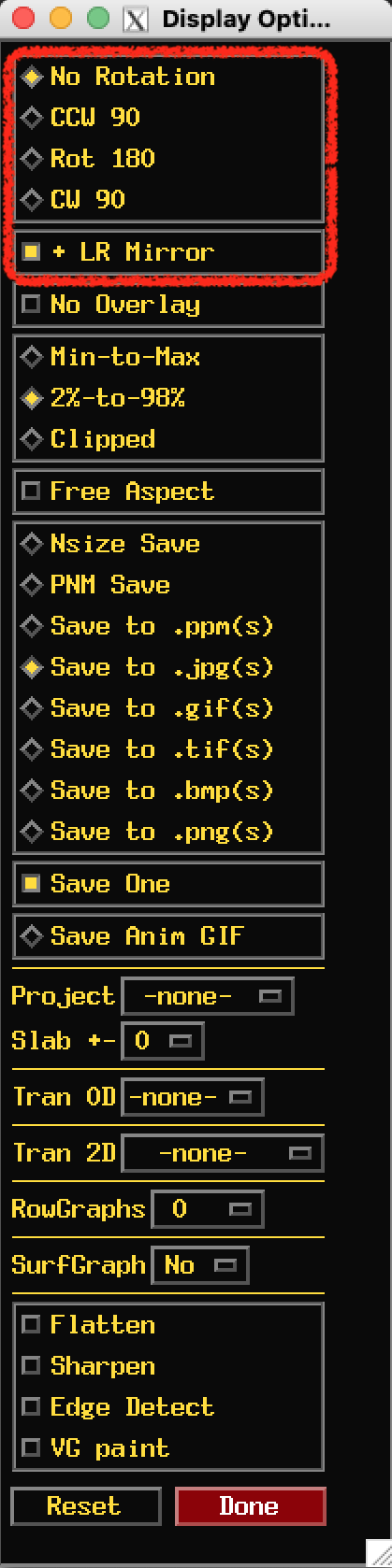
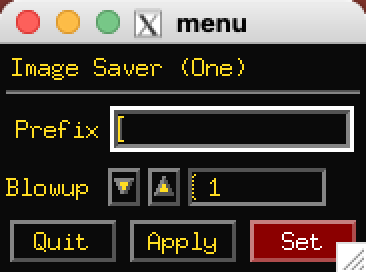
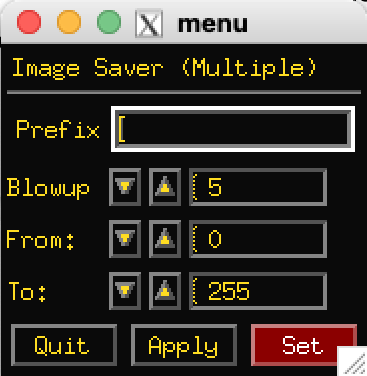
Save will save record images. (files with the same prefix will be
overwritten without warning.
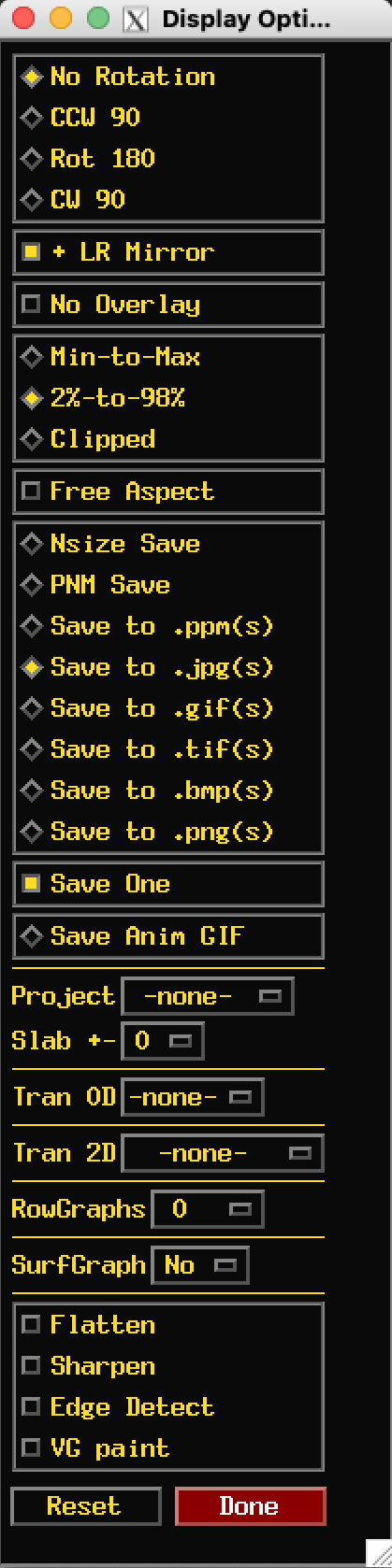
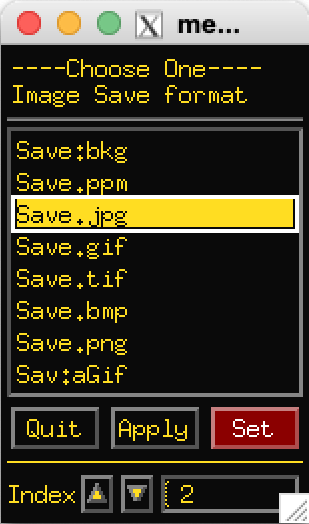
Right click on Save to change the output image format.
Your choice of formats is not saved after you close this special
viewer. So remember to change this each time you start.
aGif is a good choice. If you leave it on .jpg you will
get a single jpeg file for each item in the sequence.
You may want to set Xhairs to Off on the AFNI control panel
before recording images.
Done closes the recorded image viewer.
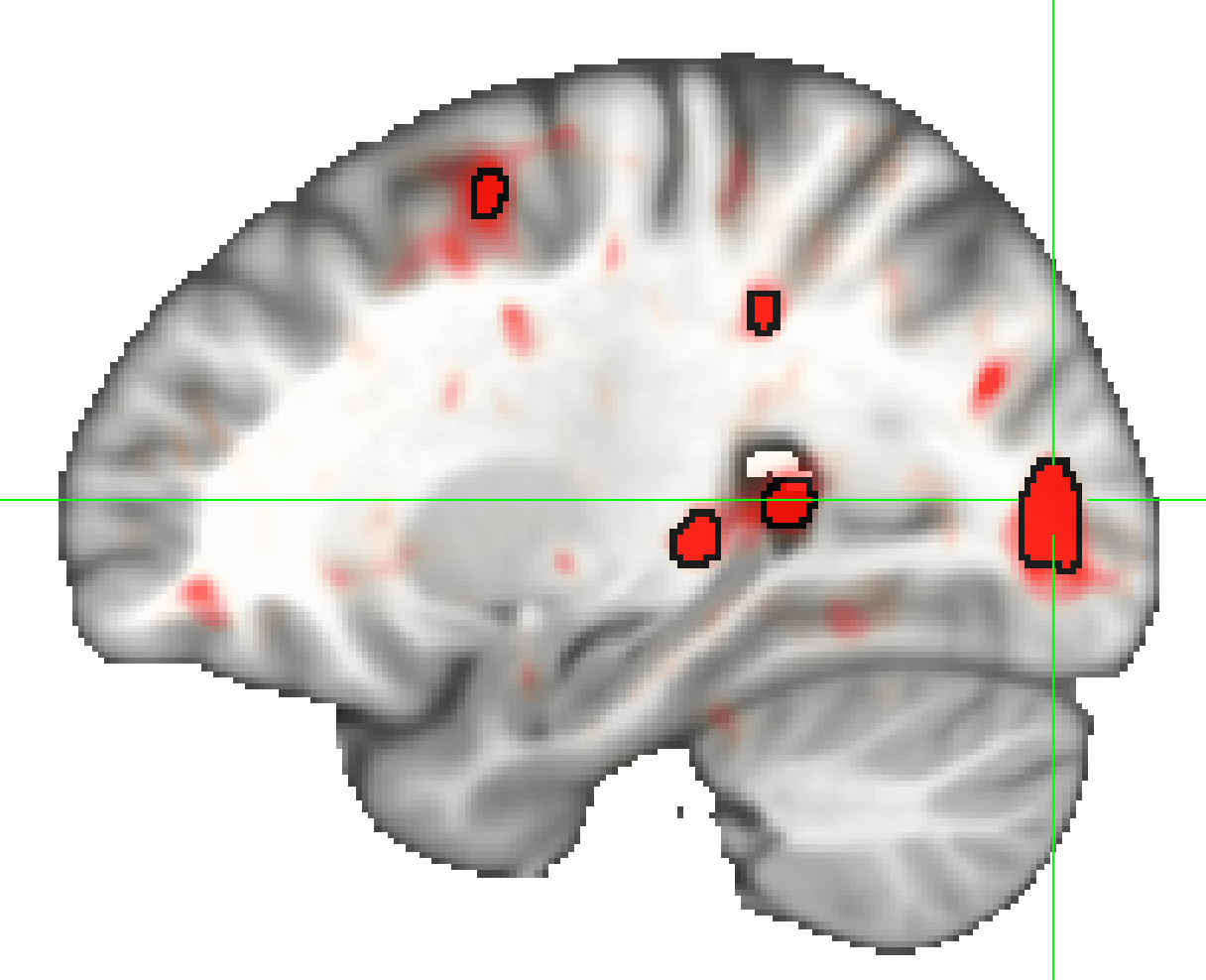
Here is a simple example output:
If Unix programs whirlgif and/or gifsicle are installed on
your system, AFNI can write GIF animations directly
(e.g., for fun Web pages).
If program mpeg_encode is installed, AFNI can write MPEG-1
animations.
Source code for these free programs is included with AFNI source
code.